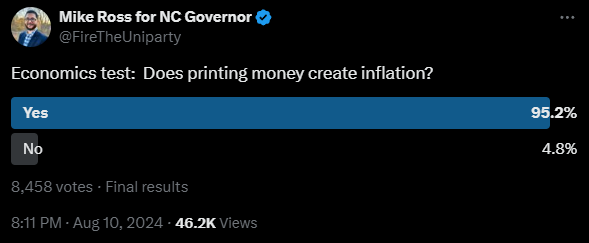
Does Printing Money Create Inflation?
The Libertarian Party candidate for governor of North Carolina posed this question on Twitter a few days ago:
The question is poorly worded, but that is mainly the fault of the way the term “inflation” has fared in common parlance. Ross probably got the poll results he desired – he was trying to reinforce the idea that increasing the supply of money results in higher prices. The issue, however, is that those who understand that relationship are also usually the ones who think inflation ought to refer to increases in the money supply. For them, the question reads, “Does increasing the money supply create increases in the money supply?” The answer to the question now depends on how one interprets “create” instead of one’s understanding of economic cause-and-effect. Indeed, many of the discerning commenters said something to the effect of “printing money IS inflation.”
Ludwig von Mises lamented these terminological shifting sands in Human Action:
The semantic revolution which is one of the characteristic features of our day has also changed the traditional connotation of the terms inflation and deflation. What many people today call inflation or deflation is no longer the great increase or decrease in the supply of money, but its inexorable consequences, the general tendency toward a rise or a fall in commodity prices and wage rates. This innovation is by no means harmless. It plays an important role in fomenting the popular tendencies toward inflationism.
First of all there is no longer any term available to signify what inflation used to signify. It is impossible to fight a policy which you cannot name. Statesmen and writers no longer have the opportunity of resorting to a terminology accepted and understood by the public when they want to question the expediency of issuing huge amounts of additional money. They must enter into a detailed analysis and description of this policy with full particulars and minute accounts whenever they want to refer to it, and they must repeat this bothersome procedure in every sentence in which they deal with the subject. As this policy has no name, it becomes self-understood and a matter of fact. It goes on luxuriantly.
I’m reminded of Ronald Reagan’s pithy way of saying the same thing: “If you’re explaining, you’re losing.” Mises realized that jumbling up the meanings of economic terms makes it easier for the state to implement disastrous policies. It’s difficult to criticize a policy when there is no consensus on what words mean.
The difficulty has only intensified over the years. Today, “inflation” is used by politicians, economists, commentators, and the public to refer to a host of different causes and even more effects.
- Robert Reich refers to inflation as the higher prices caused by corporate greed and consolidation.
- Kamala Harris, in her typical unscripted word salad, said inflation is “the cost of living going up,” and that it is “something that we take very seriously, very seriously.”
- Paul Krugman thinks about inflation through the Keynesian aggregate supply and demand framework. For him, inflation is whatever is revealed in the various official price level statistics.
- Jerome Powell also looks to the official statistics, but with an eye toward manipulating interest rates to minimize the difference between the year-over-year changes and the central bank’s two percent target.
Michael Bryan documented the evolution of the term inflation in three phases. Its original definition involved “a change in the proportion of currency in circulation relative to the amount of precious metal that constituted a nation’s money.” Later, economists started using the term to refer to increases in the supply of money relative to “the needs of trade” or the demand for money. Over the course of the 20th century, inflation became synonymous with price increases, “and its connection to money is often overlooked.”
Rothbard favored the original definition. Mises mainly dealt with the second. Modern Austrian economists make use of both definitions, but overwhelmingly reject the last. You will often hear modern Austrian economists (somewhat awkwardly) deal with the terminological problem by adding clarifiers: “monetary inflation,” “price inflation,” or “in this context, by ‘inflation’ I mean _____.”
The third definition (inflation is an increase in prices) has many serious problems. Chief among them, according to Mises, is that it conjures an
image of a level of a liquid which goes up or down according to the increase or decrease in its quantity, but which, like a liquid in a tank, always rises evenly. But with prices, there is no such thing as a “level.” Prices do not change to the same extent at the same time. There are always prices that are changing more rapidly, rising or falling more rapidly than other prices.
Another problem is that it leads the public and politicians to think that the consequences of monetary expansion can be arrested by further interventions like price controls: “While merely fighting symptoms, they pretend to fight the root causes of the evil. Because they do not comprehend the causal relation between the increase in the quantity of money on the one hand and the rise in prices on the other, they practically make things worse.”
Finally, the definition is causally naked. If inflation is an increase in prices, then anything that results in higher prices can be called “inflationary.” This became obvious in recent years when covid-era supply chain disruptions were said to have caused inflation. The same reasoning, with a dash of Marxist class conflict, allows the Robert Reichs and Elizabeth Warrens of the world to blame inflation on corporate greed. It has led to the segmentation of “inflation” by sector or industry: we have health care inflation, shelter inflation, inflation in higher education, energy inflation, and on and on. While disaggregation can be analytically useful, and often it is necessary when countering the highly-aggregated mainstream macroeconomics, this kind is not. It muddles the water regarding the nature of inflation, and it can’t capture the step-by-step process by which new money results in a “price revolution.” Fiat money inflation distorts the market as individuals receive it in exchange and then use it to increase their demands for goods produced in a variety of industries. Money goes from individual to individual, not industry to industry.
Mises was absolutely right when he concluded: “It is obvious that this new-fangled connotation of the terms inflation and deflation is utterly confusing and misleading and must be unconditionally rejected.”
Originally Posted at https://mises.org/
Stay Updated with news.freeptomaineradio.com’s Daily Newsletter
Stay informed! Subscribe to our daily newsletter to receive updates on our latest blog posts directly in your inbox. Don’t let important information get buried by big tech.
Current subscribers: