By Dhaval Joshi of BCA Research
Executive Summary
-
The value of both gold and bitcoin comes from their so-called ‘network effect’.
-
The network effect of both gold and bitcoin comes from the collective belief that they are the non-confiscatable assets to own in a fiat monetary system, as an insurance against hyperinflation, banking system failure, or state expropriation.
-
As global wealth rises, the value of the network effect of both gold and bitcoin will also rise.
-
But as bitcoin takes market share from gold, bitcoin has considerably more upside than gold.
-
Despite bitcoin’s election-fuelled rally, its 260-day complexity is not yet close to the 1.2 level that would signal the start of another crypto winter.
-
Hence, while we should expect a near-term retracement, bitcoin’s structural uptrend is intact with an ultimate destination of $200,000+
-
10-year T-bonds and Portuguese stocks are tactically oversold.
Back in 2021, I penned a report explaining why bitcoin was headed to $100,000+. Suffice to say, my $100,000+ forecast stirred a hornets’ nest, even here at BCA. The naysayers pushed back hard, claiming that bitcoin was a ‘Ponzi scheme’ or, at the very least, a dangerous bubble.
Yet three years on, my prediction has been vindicated both for its price forecast and its underlying justification. Now, with the bitcoin price closing in on $100,000, is it time to take profits? The answer depends on whether you are a trader or a long-term holder.
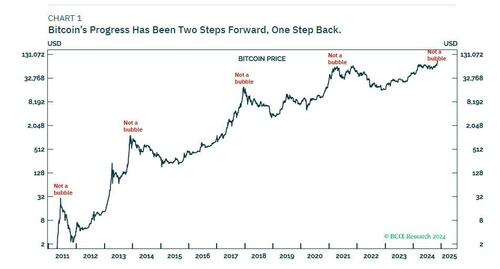
Bitcoin’s progress has always been two steps forward, one step back. After its recent surge, premised on the more ‘bitcoin friendly’ candidate winning the US presidency, we can expect some near-term retracement – as was the case in April this year. On a multiyear horizon though, bitcoin’s structural uptrend is intact and will ultimately take it to $200,000+ (Chart 1).
The Value Of Gold And Bitcoin Come From Their ‘Non-Confiscatability’
To understand the value of bitcoin we must understand the value of gold. With gold predominantly used as jewellery, many people think that the value of gold comes from its properties as a precious metal, especially the chemical inertness that keeps it eternally beautiful. But this is a misunderstanding.
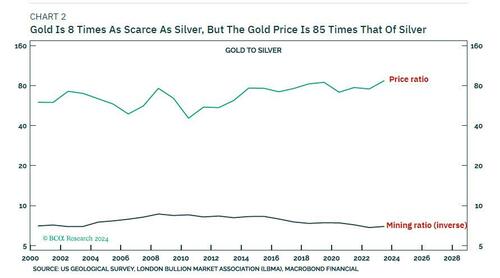
The other precious metals that are gold’s neighbours in groups 10 and 11 of the periodic table – silver, platinum, and palladium – possess identical properties to gold. This means that we can quantify gold’s value as a precious metal as being gold’s relative scarcity versus, say, silver multiplied by the price of silver.
Today, gold is roughly eight times as scarce as silver, so gold’s value as a precious metal is the price of silver, $30/oz, times eight, which equals $240/oz. This comprises just 10 percent of gold’s current market price of $2550/oz (Chart 2).
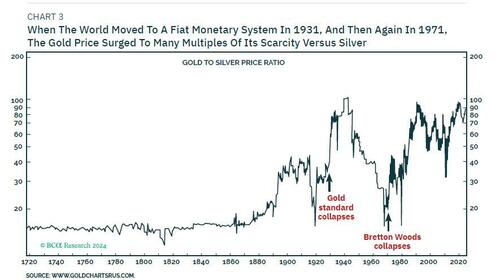
Yet for centuries, the gold price did just equal its scarcity versus silver multiplied by the silver price. The relationship ended only when the world moved to a fiat monetary system in 1931, and then again in 1971. In a fiat monetary system, the gold price surges to many multiples of its scarcity versus silver (Chart 3).
This provides the compelling proof that in a fiat monetary system, most of gold’s value comes not from its use as a precious metal. Most of gold’s value comes from the network of marginal buyers who are holding it for what I call its ‘non-confiscability’. Unlike financial assets, bank deposits, or cash, the state cannot confiscate gold via fiat monetary inflation. This is ensured by gold’s limited supply. Nor can gold be confiscated by the higher risk of a banking system failure that a fiat monetary system aggravates.
Can we justify the price of gold instead by the high cost of mining it? No, the causality runs the other way. The cost of mining gold is driven by its market price, as miners grab the largest share of its selling price that they can.
What about central bank purchases of gold? Central bank reserves also hold gold rather than foreign fiat currencies for gold’s non-confiscatability. A foreign fiat currency can be confiscated via devaluation by its government or central bank, but gold cannot.
All of which brings us to two key points:
First, given that gold’s above-ground market value is $19 trillion,1 the majority, around $17 trillion comes from the network of holders who value gold for its non-confiscatability.
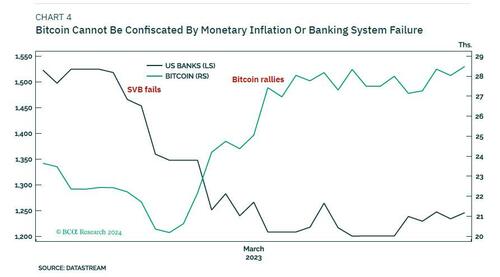
Second, just like gold, bitcoin cannot be confiscated by monetary inflation or banking system failure (Chart 4). Additionally, and
unlike gold, it is difficult for the state to confiscate it by outright expropriation. Yet bitcoin, with a market value of $1.5 trillion comprises less than 10 percent of the total market for non-confiscatable assets. As bitcoin’s share of this market increases, and the supply of bitcoins reaches its upper limit, bitcoin’s price has substantial upside.
The Value Of Bitcoin’s ‘Network Effect’ Has Substantial Upside
In essence, the value of both gold and bitcoin comes from their so-called ‘network effect’. A network effect creates a self-reinforcing cycle of value where each new user makes the network more valuable for everyone.
In the case of both gold and bitcoin, their network effect come from the collective belief that they are the non-confiscatable assets to own in a fiat monetary system. And that a certain proportion of total wealth must be held in these non-confiscatable assets as an insurance against hyperinflation, banking system failure, or state expropriation.
You might ask, what is the difference between a network effect based on collective belief and a Ponzi Scheme? The answer is that a Ponzi Scheme relies on an exponential growth of its network on a promise to get-rich-quick. Once that exponential growth ends, as it must, the value of the network collapses.
By contrast, gold’s network effect has existed in relatively stable form since 1971, and bitcoin’s network effect has existed for over ten years. And their entire raison d’être is an insurance against the get-poor-quick that comes from hyperinflation, banking system failure, or state expropriation.
The upshot is that we can value the gold and bitcoin networks as the product of three terms:
-
Global wealth
-
Global wealth share held in the non-confiscatable asset-class
-
Non-confiscatable asset-class share held in gold/bitcoin
For gold, this means that if global wealth rose by say, 20 percent in the coming 2-3 years and the global wealth share held in the non-confiscatable asset-class held constant, while bitcoin eroded the non-confiscatable asset-class share held in gold from 90 to 80 percent, then the gold price would nevertheless increase by about 7 percent. Under the same premise though, the bitcoin price would increase by about 140 percent3 to $200,000+.
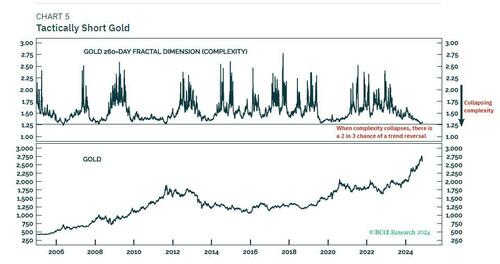
What does our proprietary analysis of price trend complexity reveal for gold and bitcoin? Gold’s 260-day price rally complexity (fractal dimension) recently reached the point of collapse that has reliably signalled tactical retracements. This justifies our current tactical short position in gold (Chart 5).
In the case of bitcoin, its major structural downtrends – so-called ‘crypto winters’ – have started when the preceding rally’s 260-day complexity collapsed to a level of 1.2 (Chart 6).
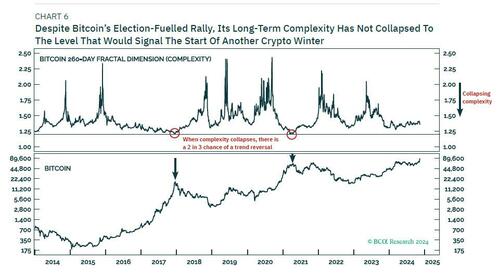
Despite bitcoin’s election-fuelled rally, its long-term complexity has not collapsed to the level that would signal the start of another crypto winter. Hence, while we should expect a near-term retracement, bitcoin’s structural uptrend is still intact with an ultimate destination of $200,000+.