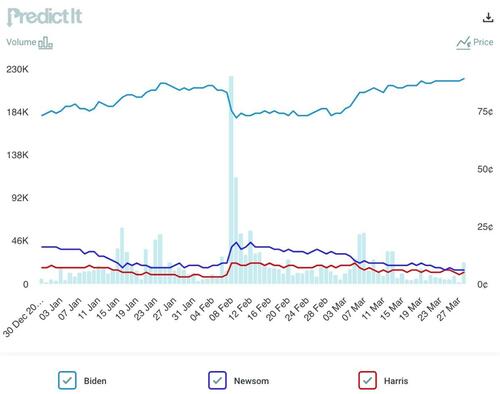
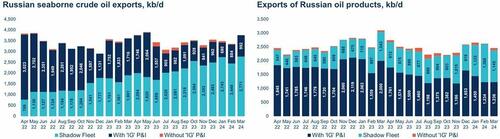
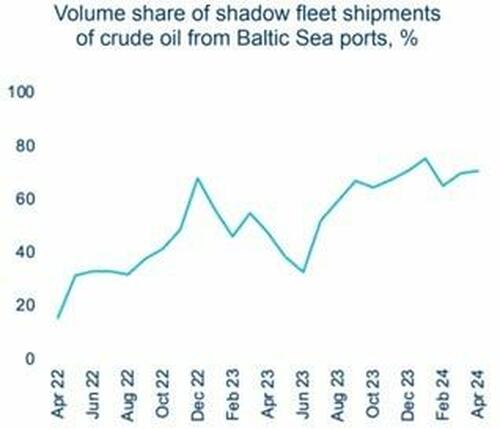
New “Engels” on Marx
Marx
by Jaime Edwards and Brian Leiter
Routledge, 224; 316 pp.
In Marx, Jaime Edwards and Brian Leiter aim to give readers who haven’t studied Karl Marx an account of the essentials of his thought and, to a lesser extent, the ideas of later Marxists as well. They argue that although some of Marx’s doctrines are wrong, others are correct; in particular, they take Marx to be unrivaled as an analyst of capitalism. In what follows, I’ll comment on a few points in the book.
Marx follows David Ricardo in contending that the exchange-value (price) of a commodity (a good or service bought and sold in the market) is the number of “socially necessary” labor hours required to produce it. This applies to labor as well. The value of labor is determined by the socially necessary labor time needed to “produce” the worker (i.e., the time needed to enable him to consume enough to sustain himself and to reproduce).
The rate at which an exchange takes place will, in equilibrium, be in strict proportion to the number of labor hours needed to produce each good. But now a problem arises. If goods exchange at equivalent values, how do capitalists earn a profit? (By “profit,” Marx means a rate of return on an investment rather than entrepreneurial gains from arbitrage). The capitalist starts with a certain amount of money, and, after a process of production, sells his product for more money than he started with. How is this possible?
Marx’s answer is that when capitalists hire workers, they buy the workers’ “labor power.” During the working day, the worker is generating value by expending labor hours on what is produced. But the employer has paid the worker only for the value of labor, the socially necessary time required to “produce” him. The gap between labor power and labor is “surplus value,” and this is the source profit and rent.
Edwards and Leiter acknowledge that this theory must be rejected. It cannot solve the “transformation problem,” despite the efforts expended on this problem by generations of Marxists. (I will spare readers an account of this). But, if the labor theory of value is dropped, the basis for Marx’s argument that capitalism will eventually come to an end and be replaced by socialism collapses.
According to Marx’s theory of historical materialism, which Edwards and Leiter deem his most significant contribution, the “forces of production”—roughly the technology and creativity available at a particular time—determine the “relations of production,” roughly, how production is organized into different economic classes. The relations of production will tend to be those best-suited to develop the forces of production. As the forces of production continue to develop, a point will be reached when the relations of production will become “fetters,” and a revolution will usher in new relations of production.
Marx maintains that this is what will happen to capitalism. For reasons stemming from the labor theory of value, the rate of profit tends to fall, and this leads capitalists to “squeeze” workers until they become “immiserated.” When conditions get bad enough and workers think a revolt is feasible, capitalism will be overthrown and replaced by socialism.
But, without the labor theory of value, Marx has no argument for the falling rate of profit. Must we then abandon the view that capitalism is eventually unsustainable?
Not so fast, say Edwards and Leiter. We can get to the same conclusion in a different way. To make a profit, it is not enough for a capitalist to produce something with a higher selling price than its cost. He must sell the product. But, as new technologies develop, workers are displaced and lose their buying power, unless they can find another job, which is often difficult. Additionally, capitalists will try to outsource labor, further reducing workers’ buying power, and to replace human workers with automated devices that do not require payment at all. Because of the decreased purchasing power of workers, they will be unable to buy enough to enable employers to sell their products.
The authors are right that capitalists want to minimize their wage costs. But it does not follow from this that they can successfully drive wages below the workers’ marginal product. The argument that they can rests on the view that capitalists have more bargaining power than workers. A worker offered a low wage cannot realistically hold out for better terms because he must have a job to survive, but the employer can readily replace him with someone else from the “industrial reserve army.” What this argument ignores is that if an employer offers a worker a wage below his marginal product, a competing firm will have an incentive to hire him away. To get around this point, we can postulate an agreement among employers not to undercut each other’s wage offers, but that seems implausible. So far as automation is concerned, Edwards and Leiter acknowledge that, in past instances, automation has created more jobs than it has destroyed; but this time, they suggest, things will be different. Why?
Austrians would fault the “spending” argument in another way as well. The whole assumption that an economy requires a level of spending for sustainability must be rejected. If prices are flexible—adjusting to changes in supply and demand—all is well. Here the work of W.H. Hutt is fundamental.
In Marx’s view, socialism will eventually supplant capitalism, after the proletariat reaches the breaking point. But Marx has little to say about how socialism is supposed to work. And, in fact, Ludwig von Mises’s calculation argument shows that, without capitalist market prices, an economy would collapse into chaos. The “centrally planned” economies, established after the Bolshevik Revolution, were able to use world market prices in their plans, so they cannot be cited as a refutation of Mises’s argument.
Some “analytical Marxists,” most notably G.A. Cohen, have responded to the weaknesses in Marx’s theoretical edifice by moving to the normative realm. Socialists should no longer argue that the coming of socialism is inevitable but rather that it is required by morality. Edwards and Leiter make a good case that Marx disdained appeals to morality. Cohen disagreed, but even if he was wrong about what Marx thought, he could still say, “Even if I’ve got Marx wrong, so what?”
Originally Posted at https://mises.org/
Stay Updated with news.freeptomaineradio.com’s Daily Newsletter
Stay informed! Subscribe to our daily newsletter to receive updates on our latest blog posts directly in your inbox. Don’t let important information get buried by big tech.
Current subscribers: